Lava Molds
Lava Casts - Tree Molds - Tree Moulds



Lava Mold Caves are caves caused by objects which are enclosed by a lava flow. While the heat of the lava causes the object to burn, if it is wet and big enough, it will also cool down the lava surrounding it. The lava gets solid, and when the object is burned away there is an empty mold. Later, when the eruption has ended, the lava flows away leaving the empty molds open on the surface. If the lava does nor flow away, it solidifies around the mold and they form well like pits. There is also the possibility that a fissure opens and sprays fountains of lava into the air. The falling lava coats trees and again the insides burn out leaving a lava mold around the tree. Sometimes even trees trunks lying on the ground are covered by a lava flow, the result is a horizontal tube. And if the resulting tube is big enough for a human to enter, it is called a cave.
Most lava molds are tree molds, because it is quite common that a lava flow covers a forest, so the term Tree Mold is also commonly used. Actually it is the less exact but more commonly used term. But in general any plant, animal or other thing which burns or decays afterwards will leave such a cave. There are numerous tree molds over the world, and there is even one cave which is thought to be the mold of a huge rhinoceros, the famous Blue Lake Rhino. All in all this are probably the rarest caves on earth.
Many such objects are very interesting, even if they can hardly be called caves. So there were a very large number of such cavities in Pompeii that were human-shaped. Bone remains were found in a few. By pouring in plaster you could get real-life sculptures, or rather "full-size" death masks. Something like that is hardly considered a cave, if the faded guy wasn’t really obese, the cavity is simply too small.
In addition to hollow molds, trees also have filled molds. The form fills with lava as the eruption continues. Weathering is later very efficient in separating the shell and the core, so the cast of a tree is suddenly outdoors. Or the tree is preserved because it does not burn due to lack of oxygen. Later it petrifies through groundwater and after the basalt is weathered aways, the petrified tree remains.
- Pavel Bella, Ľudovít Gaál (2015): Tree mould caves within the framework of cave genetic classification, Nature Conservation 63: 7-11. online
 Funatsu Tainai
Funatsu Tainai Blue Lake Rhino Cave
Blue Lake Rhino Cave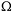 Mauna Loa Tree Molds
Mauna Loa Tree Molds Puna Tree Molds
Puna Tree Molds Trail of Two Forests
Trail of Two Forests Skalky skřítků
Skalky skřítků
Literature
- Pavel Bella, Ľudovít Gaál (2007): Tree mould caves within the framework of cave genetic classification, Nature Conservation 63:7-11, July 2007. researchgate.net
 Search DuckDuckGo for "Tree Molds"
Search DuckDuckGo for "Tree Molds" Lava tree mold - Wikipedia (visited: 07-MAY-2020)
Lava tree mold - Wikipedia (visited: 07-MAY-2020) Lava Trees and Tree Molds (visited: 07-MAY-2020)
Lava Trees and Tree Molds (visited: 07-MAY-2020) Index
Index Topics
Topics Hierarchical
Hierarchical Countries
Countries Maps
Maps